 इस पर फोन करें :
+86 18681515767
इस पर फोन करें :
+86 18681515767
 ईमेल :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
ईमेल :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
 इस पर फोन करें :
+86 18681515767
इस पर फोन करें :
+86 18681515767
 ईमेल :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
ईमेल :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
01. हमारे उत्पाद
गरम सामानशेन्ज़ेन jietong प्रौद्योगिकी के सह।, लि। एक हाई-टेक कंपनी है जो रेडियो फ्रीक्वेंसी आइडेंटिफिकेशन (आरएफआईडी) के विकास, उत्पादन और बिक्री पर ध्यान केंद्रित करती है।
हमेशा एक कदम और!
शेन्ज़ेन Jietong प्रौद्योगिकी कं, लिमिटेड एक उच्च तकनीक कंपनी है जो R & D, उत्पादन और UHF RFID हार्डवेयर की बिक्री पर ध्यान केंद्रित करती है। जीतोंग की अपनी आर एंड डी टीम है जो इंजीनियरों के पास 10 से अधिक वर्षों का आर एंड डी अनुभव है। ग्राहक को सर्वोत्तम सेवा और उत्पाद प्रदान करने के लिए, जीतोंग परियोजना, बिक्री के बाद सेवा और प्रौद्योगिकी समर्थन के लिए संपूर्ण समाधान प्रदान करने के लिए निरंतर विकास में है। Jietong में मुख्य उत्पाद लाइनें हैं जिनमें UHF RFID Impinj R2000/TM200 मल्टी-टैग रीडिंग रीडर , UHF RFID सिंगल टैग रीडिंग रीडर , UHF RFID लॉन्ग रेंज रीडर , UHF RFID मिडिल रेंज रीडर , UHF RFID डेस्कटॉप रीडर/राइटर , UHF RFID रीडर मॉड्यूल शामिल हैं। , यूएचएफ आरएफआईडी हैंडहेल्ड रीडर , यूएचएफ आरएफआईडी एंटीना , यूएचएफ आरएफआईडी कार्ड और टैग इत्यादि। जीतोंग में उपयोगकर्ताओं की सर्वोच्चता का सिद्धांत है, और बाजार उन्मुख, नई तकनीक और उच्च गुणवत्ता पर निर्भर करता है, हम अपने ग्राहकों को नवीनतम तकनीक, सर्वोत्तम उत्पाद, प्रतिस्पर्धी, ईमानदारी से सेवा प्रदान करेंगे। हमने खुद को अपने ग्राहकों और आपूर्तिकर्ताओं के व्यवसायों के एक विश्वसनीय, अभिनव और भरोसेमंद हिस्से के रूप में स्थापित किया है।

02. हमारा चयन क्यों
हमारे लाभशेन्ज़ेन jietong प्रौद्योगिकी के सह। लि।, एक उच्च तकनीक वाली कंपनी है जो रेडियो फ्रीक्वेंसी आइडेंटिफिकेशन (आरएफआईडी) के उत्पादन और बिक्री पर केंद्रित है। चीजों के इंटरनेट के उह आरएफआईडी श्रृंखला के पाठक में विशेष पेशेवर। jietong की अपनी r & d टीम है, जो इंजीनियरों के पास 10 वर्ष से अधिक के r & d अनुभव है। ग्राहक को सर्वोत्तम सेवा और उत्पाद प्रदान करने के लिए, jietong परियोजना के लिए संपूर्ण समाधान, बिक्री के बाद सेवा और प्रौद्योगिकी सहायता प्रदान करने के लिए निरंतर विकास में है।jietong की मुख्य उत्पाद लाइनें हैं, जिसमें uhf rfid मॉड्यूल, rfid हैंडहेल्ड रीडर, uhf rfid रीडर, कार पार्किंग मिडिल रेंज rfid रीडर, uhf एक्सेस कंट्रोल रीडर, uhf एंटीना, uhf कार्ड और टैग इत्यादि शामिल हैं।jt uhf rfid रीडर पहले से ही वाहन प्रबंधन में गहनता से उपयोग किया जाता है, पर्यावरण का उपयोग कारखाने के लिए कर्मचारी प्रबंधन, गोदाम के लिए भार प्रबंधन, गोदाम और वाहन के लिए अभिगम नियंत्रण, वस्त्र प्रबंधन, तंबाकू रसद प्रबंधन, बुद्धिमान पुस्तकालय प्रबंधन, उत्पादन लाइन पहचान प्रबंधन, परिसंपत्ति में शामिल है। प्रबंधन आदिjietong में उपयोगकर्ताओं की सर्वोच्चता का सिद्धांत है, और यह बाजार-उन्मुख, नई तकनीक और उच्च गुणवत्ता पर निर्भर करता है, हम नवीनतम तकनीक, सर्वोत्तम उत्पाद, प्रतिस्पर्धी, हमारे ग्राहकों को ईमानदारी से सेवा प्रदान करेंगे।
03. परियोजना के मामले
समाधान और मामलायह समाधान पृष्ठ ग्राहकों को जीतोंग टेक्नोलॉजी के उत्पादों का उपयोग करके एप्लिकेशन इंस्टॉल करने और प्रबंधित करने की समस्या को हल करने में मदद करता है। निम्नलिखित शामिल हैं: वाहन प्रबंधन UHF व्यक्तिगत प्रणाली प्रबंधन उत्पादन लाइन प्रबंधन तार्किक प्रबंधन परिसंपत्ति प्रबंधन गोदाम प्रबंधन पर्यावरण स्वच्छता वाहनों का प्रबंधन बुद्धिमान किताबों की अलमारी प्रबंधन
RFID Technology in the Renewable Energy Sector: Applications and Opportunities 1. Introduction As the global renewable energy industry expands, efficient asset management, supply c...
अधिक पढ़ें
वाहन प्रबंधनचीन की अर्थव्यवस्था के चिकित्सीय विकास के साथ, लोगों के जीवन स्तर में वृद्धि हो रही है, कार का कुल स्वामित्व भी तेजी से बढ़ने लगा। वर्तमान में, वाहन प्रबंधन में मुख्य र...
अधिक पढ़ें
उह rfid कार्मिक प्रबंधन प्रणाली>> सिस्टम अवलोकनलंबी दूरी के कर्मचारी प्रबंधन प्रणाली uhf आरएफआईडी प्रौद्योगिकी, इंटरनेट प्रौद्योगिकी और अनुप्रयोग-विज्ञान की…यह समय उपस्थिति प्रणाली...
अधिक पढ़ें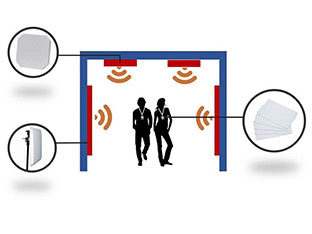
उत्पादन लाइन प्रबंधनबेहतर गुणवत्ता वाले उत्पाद बनाने के लिए, उत्पादन लागत को कम करते हुए और iso9000 की आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करने के लिए, निर्माता अधिक बारीकी से उत्पाद जानकारी और कंट...
अधिक पढ़ें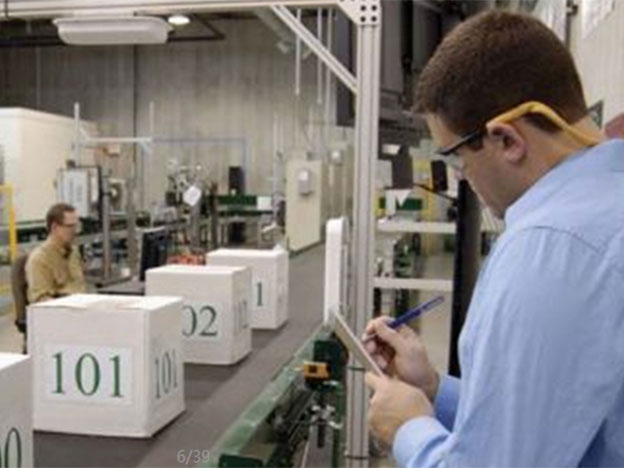
एजीवी ट्रॉली ट्रैक मार्गदर्शन प्रबंधनविनिर्माण स्तर और बढ़ती हुई मांग के साथ, कई तरह की लॉजिस्टिक्स प्रणाली को कई चुनौतियों का सामना करना पड़ रहा है, जैसे कि लॉजिस्टिक्स सिस्टम टर्...
अधिक पढ़ें
संपत्ति आरएफआईडी प्रबंधन प्रणालीसिस्टम सारांशपरिसंपत्ति प्रबंधन, वितरण, भंडारण, निपटान, आदि सहित परिसंपत्ति प्रबंधन को मैन्युअल रूप से लागू करने का तरीका कभी भी उद्यमों और संबद्ध स...
अधिक पढ़ें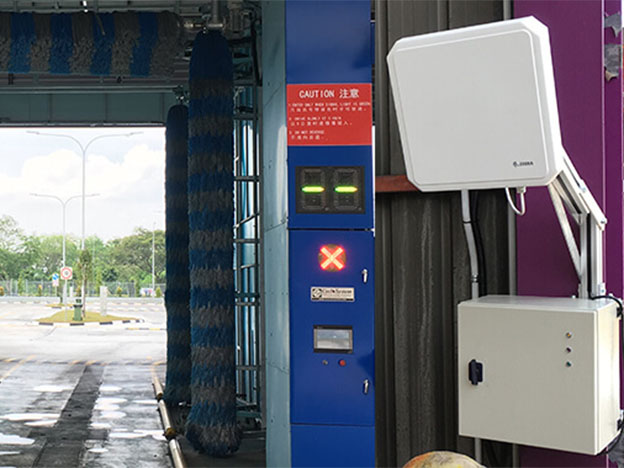
04. आयोजन
ताज़ा खबरशेन्ज़ेन jietong प्रौद्योगिकी के सह।, लि। एक हाई-टेक कंपनी है जो रेडियो फ्रीक्वेंसी आइडेंटिफिकेशन (आरएफआईडी) के विकास, उत्पादन और बिक्री पर ध्यान केंद्रित करती है।


05. मुफ्त परामर्श
एक संदेश छोड़ेंयदि आप हमारे उत्पादों में रुचि रखते हैं और अधिक जानकारी जानना चाहते हैं, तो कृपया यहां एक संदेश छोड़ दें, हम जैसे ही हम कर सकते हैं, हम आपको जवाब देंगे।

फ़ोन : +86 18681515767
Whatsapp : +8618681515767

ईमेल : marketing@jtspeedwork.com

12/F, Building A, No. 6, Shiben Road, Shiyan Street, Bao'an District, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China-518108
कॉपीराइट © 2026 Shenzhen Jietong Technology Co.,Ltd. सभी अधिकार सुरक्षित.

ipv6 नेटवर्क समर्थित